Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key
Introduction
- Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key In Ubuntu
- Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key Github
- Git Windows Generate Ssh Key
- Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key Mac
- Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key Windows
- List Ssh Keys Git Bash
SSH (Secure Shell) allows secure remote connections between two systems. With this cryptographic protocol, you can manage machines, copy, or move files on a remote server via encrypted channels.
There are two ways to login onto a remote system over SSH – using password authentication or public key authentication (passwordless SSH login).
Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key In Ubuntu
Setting up Git can be tricky on Windows compared to Linux or Mac, but if you follow the steps in this guide, you should have no problems using Git on Windows. We’ve done the hard work and chosen between the multiple options at key steps to help make things easier for you. Git uses SSH keys to securely access your repositories, and in Windows SSH keys are often searched on the wrong path when you try to use Git. If you use an older version of msysGit, you may encounter a step called “Choosing the SSH executables”. If you encounter that dialog, we recommend that you choose the “Use OpenSSH” option. Ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C 'your github's email' # Creates a new ssh key # Generating public/private rsa key pair. This will generate a key for you.You have to copy that and insert into your Github's account (just one time). Steps how to do It. Generating Your SSH Public Key Many Git servers authenticate using SSH public keys. In order to provide a public key, each user in your system must generate one if they don’t already have one. Adding your SSH public key to GitLab. Create and add your SSH key pair. It is best practice to use Git over SSH instead of Git over HTTP. In order to use SSH, you will need to: Create an SSH key pair; Add your SSH public key to GitLab. Creating your SSH key pair. Go to your command line. Follow the instructions to generate your SSH key pair. Adding your SSH public key to GitLab. GitLab and SSH keys. Git is a distributed version control system, which means you can work locally. In addition, you can also share or “push” your changes to other servers. GitLab supports secure communication between Git and its servers using SSH keys. Apr 12, 2018 SSH-key-based authentication provides a more secure alternative to password-based authentication. In this tutorial we'll learn how to set up SSH key-based authentication on an Ubuntu 16.04 installation.
In this tutorial, you will find out how to set up and enable passwordless SSH login.
- Access to command line/terminal window
- User with sudo or root privileges
- A local server and a remote server
- SSH access to a remote server via command line/terminal window
You may already have an SSH key pair generated on your machine. To see whether you have SSH keys on the system, run the command:
If the output tells you there are no such files, move on to the next step, which shows you how to generate SSH keys.
In case you do have them, you can use the existing keys, back them up and create a new pair or overwrite it.
1. The first thing you need to do is generate an SSH key pair on the machine you are currently working on.
In this example, we generate a 4096-bit key pair. We also add an email address, however this is optional. The command is:
Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key Github
2. Next, type in the location where you want to store the keys or hit Enter to accept the default path.
3. It also asks you to set a passphrase. Although this makes the connection even more secure, it may interrupt when setting up automated processes. Therefore, you can type in a passphrase or just press Enter to skip this step.
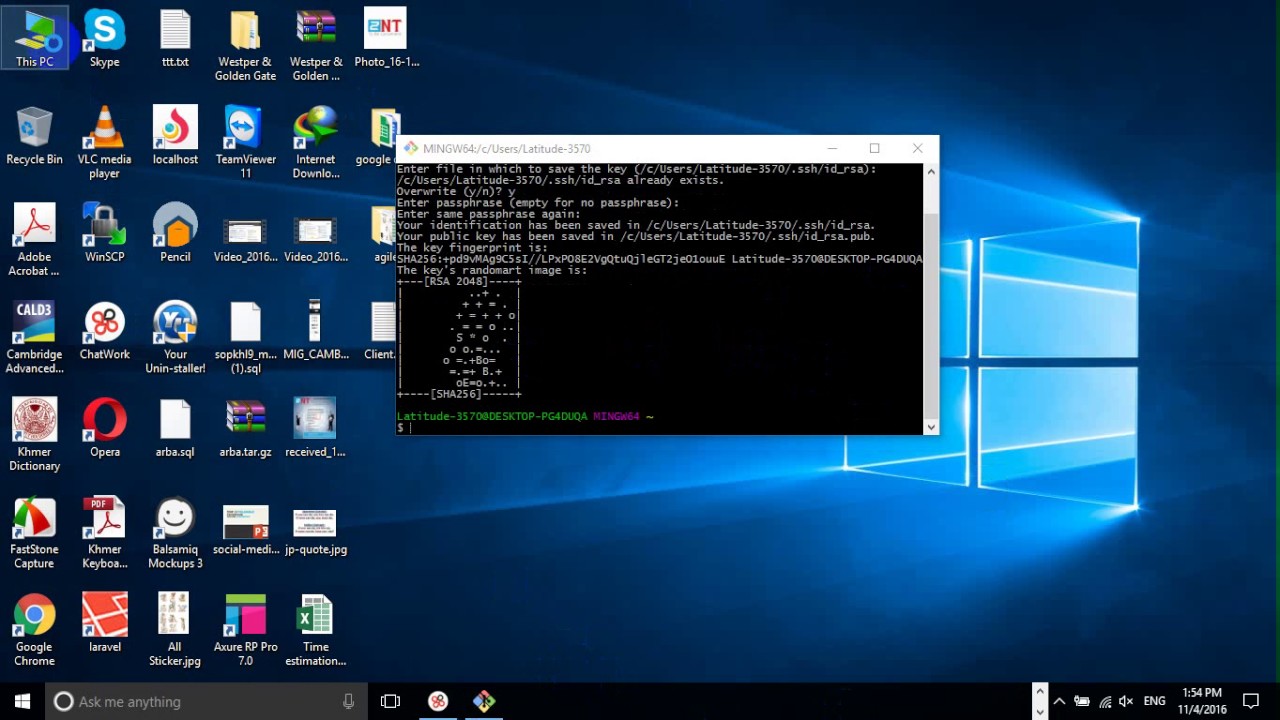
4. The output then tells you where it stored the identification and public key and gives you the key fingerprint.
5. Verify you have successfully created the SSH key pair by running the command:
You should see the path of the identification key and the public key, as in the image below:
You can upload the public SSH key to a remote server with the ssh-copy-id command or the cat command. Below you can find both options.
Option 1: Upload Public Key Using the ssh-copy-id Command
To enable passwordless access, you need to upload a copy of the public key to the remote server.
1. Connect to the remote server and use the ssh-copy-id command:
2. The public key is then automatically copied into the .ssh/authorized_keys file.
Another way to copy the public key to the server is by using the cat command.
1. Start by connecting to the server and creating a .ssh directory on it.
2. Then, type in the password for the remote user.
3. Now you can upload the public key from the local machine to the remote server. The command also specifies that the key will be stored under the name authorized_keys in the newly created .ssh directory:
With the SSH key pair generated and the public key uploaded to the remote server, you should now be able to connect to your dedicated server without providing a password.
Check whether the setup works by running the command:
The system should directly log you in to the remote server, no password required.
Note: Once you verify that you can SHH into the remote serve without a password, consider disabling SSH password authentication altogether. It will add another layer of security and secure your server from brute-force attacks.
Optional: Troubleshooting Remote Server File Permissions
File permissions on the remote server may cause issues with passwordless SSH login. This is a common issue with older versions of SSH.
Git Windows Generate Ssh Key
If you are still prompted for a password after going through all the steps, start by editing file permissions on the remote server.
- Set permissions 700 for the .ssh directory.
- Set permissions 640 for the .ssh/authorized_keys directory.
Edit file permissions with the following command:
Enter your password when prompted. There will be no output if the action was successful. The issue should be resolved now.
If you want to automate updates and other tasks, or seamlessly SSH into a remote server, you should enable passwordless SSH login.
Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key Mac
The instructions outlined in this article should have helped you to do so.
For more SSH commands, check out these 19 common SSH commands in Linux with examples.
Next you should also read
When establishing a remote connection between a client and a server, a primary concern is ensuring a secure…
Hackers are always on the lookout for server vulnerabilities. Minimize risks and be confident your data is…
Using Git Bash To Generate Ssh Key Windows
The article covers the 5 most common and efficient ways to secure an SSH connection. The listed solutions go… /who-generates-a-session-key.html.
List Ssh Keys Git Bash
Rsync is a Linux tool that allows you to transfer data over SSH to a remote server securely. Use the options…